The sales funnel describes the phases that a potential customer goes through before buying a product or service. This goes hand in hand with the customer journey, in which the buyer approaches the purchase one step closer with each phase.
In sales, this is referred to as a sales funnel, since the number of interested parties is high at the beginning. At the end, however, the number of those who actually buy the product or service is significantly lower. This is a normal process.
There are methods to optimize the sales funnel or customer journey so that the original potential buyer end up becoming customers.
The problem is that most companies don’t have concrete data regarding the customer journey or sales funnel, nor do they know the reasons why potential buyers don’t want to take the step from one stage to the next.
Below you will learn how to achieve customer journey / sales funnel optimization in 6 steps:
1. Determine phases of the Sales Funnel
The first step is to describe the phases that are important for the company in question. Example:
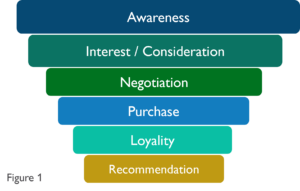
Depending on the company or department, other more detailed (or different) phases may also be important for analysis, such as: Contract conclusion, order, payment, etc.
2. Determine the actual state of the individual phases
Once the phases are defined, the ACTUAL state of each phase must be measured. Development and success can only be measured if the ACTUAL state is known.
Some parameters can be obtained from internal sources, e.g. how many customers purchased and/or re-purchased, or how many contract negotiations there were. For external parameters such as awareness, interest/consideration, referral (NPS), etc., it is important to rely on concrete and professionally-collected data instead of just estimating the values. It is indispensable that the data represent the actual customer view.

3. Identify the reasons for barriers between phases
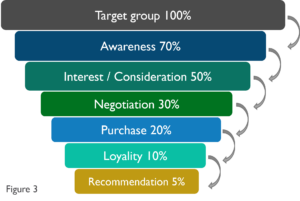
Let’s look at the example in figure no. 2:
Brand awareness within the target group is 70%, but only 20% buy the product/service and only 10% buy it again.
The company must take measures to continuously optimize the results in each individual phase.
Here, the right decisions can only be made if it is known exactly which barriers prevent the potential customer from moving from one phase to the other.
The important question here is: WHY? This question must be clarified for the transition from each phase to the next: Why do 70% of our target group know us, but why are only 50% interested in our services?
Why do 50% of potential customers consider buying but are not interested in negotiating with our sales people?
Example:
Through a market research study, the company learns that many of the customers who are familiar with the brand do not bother to find out more information, because they think the product is too expensive for them and that they could not afford it anyway. If you get even more in-depth insights and know why customers think this way, you can take concrete action to counteract this in your brand communication.
4. Define optimization targets per phase
If the company already has a concrete picture of the ACTUAL state and the barriers between the phases are also known, SMART goals can be set.
S: specific
M: measurable
A: accepted
R: realistic
T: terminated
The goals can be defined realistically, since concrete reasons are known.
5. Define measures for each phase
As soon as the KPIs and the goals have been established, measures are defined and the operational steps, including timing and the desired output, are determined. In relation to the action plan, it must also be determined how and when the results will be measured.
6. Outcome measurement
The goals were defined as SMART goals, i.e. they are measurable and scheduled. In order to be able to derive the success of the measures, it is important to measure the results after this scheduling in order to check the success of the measures. Successful measures are further implemented, less successful ones are readjusted.
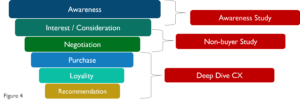
Studies for optimization in the phases
For the example used in this article, a company would need the studies shown in figure no.4:
With ClaralytiX, the analysis software tool from TEMA-Q GmbH, all departments involved can evaluate the quantitative and qualitative data in a simple and transparent way. The qualitative data is available in the form of original statements from customers on the individual purchase phases. This captures the deeper insights described under point 2.
Optimizing the sales funnel / customer journey is an ongoing task, as market conditions change just as much as the competition, customer wishes, and customer opinions. A company should therefore go through steps 1 to 6 at regular intervals.
Successful DAX companies that work with TEMA-Q book the studies mentioned in figure no.4 to analyze the individual points of contact along the customer journey.
Are you interested in further possible applications of our services to optimize your sales area? Then read our article “The Riddle’s Solution – A short story about inconclusive reversed sales – Part I“!
We are happy to support you with consulting, conception and implementation. Click here to make an appointment or contact us.
Tel: 05372-9780-19
Author:
Jacqueline Pirkelbauer – International Sales Director

